What is Jobs-to-be-Done
“Your customers are not buying your products. They are hiring them to get a job done.”
CLAY CHRISTENSENHarvard Business School
How Would You Beat Apple and Google?
A good way to test if a method and theory will work is to apply it to a real-world situation. Imagine you are on a product, marketing, or sales team and your mission is to beat Apple and Google Maps? How would you do it? How would you implement the Jobs-to-be-Done framework? In the introductory video below, we show you how you could use Jobs Theory and our methods to beat Apple and Google Maps. This seems like an impossible task since Apple and Google have about 100% market share in this market and they are fierce competitors with combined $2 Trillion (yes Trillion with a T) market caps and $200 Billion in cash. But it is possible by focusing on how and why customers struggle to get their job done when using Apple and Google Maps. This video is a great way to start with JTBD. It includes detailed examples of how to use the method to beat your competitors.

How to define your customer
Your customer is the key to your success. Learn how to avoid lethal customer definition mistakes that result in your competitors stealing your customers and your market share.
TRADITIONAL APPROACH
Your Customer Uses or Purchases Your Product
To understand your market, you need to understand your customers in depth. Who are your customers? How should you define them?
Many tech companies define the customer as a "user" i.e. the person who uses their product. This seems to make sense because that's who you're designing the experience for--the person who will actually interact with your product.
Another way to define customers is to use the dictionary definition: a person who purchases a product or service. This also seems logical, since getting someone to purchase your product is how you generate revenue.
But the person who uses your product may not be the person who purchases it.
For example, an ultrasound tech in a healthcare facility is the user of an ultrasound machine, but they don't decide to purchase it. The purchasing responsibility belongs to a hospital administrator. Meanwhile, were ultrasound machines invented so techs could be employed? Probably not. They were probably invented because doctors needed to better understand patients' conditions.
So who is the key customer?
Knowing who your target customers are and understanding them in-depth is key to determining the Jobs To Be Done in a specific market.
The ultrasound tech using the machine, the hospital administrator who decided to purchase it, the doctor who uses the ultrasound images to learn about the patient's condition, or the patient?
JOBS-TO-BE-DONE
Understanding Your Market’s Three Types of Customers
The key customer in any market is the person who benefits from getting the job done. This is who we call the “job beneficiary.” The job beneficiary is the critical customer in your market because they have the most to gain from the job-to-be-done being satisfied by your product. The second customer to consider is the "job executor". This is the person who helps execute the job on behalf of the beneficiary. For example, IT managers help employees use business software by installing it on company servers. The third customer to consider is the purchase decision maker. For example, finance executives will often decide which software to purchase based on financial and budgeting considerations.
In consumer markets, the job beneficiary, executor, and purchase decision maker are frequently the same person. A consumer benefits from “getting to a destination on time”, they execute this job by driving themselves, and they make the decision to purchase products and services to get the job done.
Medical markets are the most extreme example of the differences between job beneficiaries, executors and purchasers. Every medical product and service is ultimately designed to help patients. This is why medical markets exist: because patients need to get medical jobs done including optimizing their health, curing a health condition, and diagnosing a health condition. But patients rarely execute their own medical procedures and rarely purchase them on their own because they use insurance. For example, in order to obtain a blood sample to diagnose their health a patient (the job beneficiary) goes to a phlebotomist (the job executor) to get a blood sample, and the procedure is paid for by the insurance company (the purchaser).
It is critical to distinguish between beneficiaries, executors, and purchasers when building your product roadmap because if you target the wrong customers, you put your company at risk that a competitor takes your market share.
For example, before software-as-a-solution products, IT departments installed CRM software for salespeople. Salespeople use CRM systems to get the job done of “acquiring new customers.” Salespeople are the job beneficiaries in this market because they benefit from getting the job done with software. IT managers are the job executors who help salespeople acquire customers by installing and maintaining software. But once SaaS products were available, IT managers, the job executors, were unnecessary.
With JTBD, you can map beneficiaries, executors, and purchasers in your market to ensure you are targeting the right customers. This means that your customer and their needs decide what should be in your roadmap, not characteristics or personal opinions. JTBD removes the subjectivity so you and your team can measure what matters to your customers.
EXAMPLE
Who is The Customer for Apple & Google Maps?
Let’s look at an example, with Apple and Google Maps. Who are the customers to target in this market? The underlying Job-to-be-done is to get to a destination on time. This example shows why creating customer personas to define your customers can be flawed. Let’s say you create two personas, Kate, is younger, urban with a college degree. Paul is older, rural, and has a high school education. Could the two very different customers with very different personas and characteristics both struggle to get to a destination on time in the same way?
The answer, of course, is yes. And the reason they each struggle has nothing to do with their persona characteristics. It has to do with the nature of how they execute the job. In this case, they both struggle to get to destinations on time because they both make frequent and unfamiliar stops. In other words, these two very different customer personas actually have the same unmet customer needs in this market. If you defined your customers in this example using personas, you would miss a large segment of customers who are underserved and likely looking for a new solution.
If you are defining your customer, make sure you identify the three different customers: the job beneficiary, the job executor, and the purchase decision maker. In consumer markets, these are all often the same person. In complex markets, you need to identify all three. For example, in the medical JTBD of “obtaining a blood sample” the patient is the beneficiary, the phlebotomist is the executor, and the insurance company is the purchaser.
If you were developing a product in the market for obtaining a blood sample and you target the phlebotomist, you risk a competitor developing a solution for the patient that enables them to take their own blood sample without a trained expert. And this is exactly what is happening in this market.
Learn the JTBD Market Definition Technique:
.webp)

How to define your market
In business, the market always wins, so defining your market correctly is critical to your success. JTBD shows that most companies get this wrong. Defining your market incorrectly can destroy equity value and ruin your company.
TRADITIONAL APPROACH
Products Define Markets
Defining your market using your product is very common. In fact, this is how it is taught in business school textbooks. But history is full of examples of product-based market definitions leading companies to build failed product roadmaps.
For example, Blackberry thought there was a market for keyboard devices and they built a product roadmap based on keyboards. Britannica thought there was a market for encyclopedias and built a product roadmap based on content for bound volumes of books. And Kodak thought there was a market for film and built a product roadmap based on improving the quality of film. At first product-based market definitions seem to make sense, since people were buying a lot of mobile keyboard devices, encyclopedias, and film.
But here is the flaw: products always change. This is a key concept in Jobs Theory: unlike products, your customer’s goal, their JTBD, does not change. This is why you should define your market and build your product roadmap using your customer’s job rather than your product. Because a JTBD is a stable target to hit.
JOBS-TO-BE-DONE
Your Market Is Your Customer's Job-To-Be-Done
Defining your market using your customer Jobs-to-be-Done has profound implications for your product roadmap. Think of your product not as something a customer is buying, but as something that is helping them solve a problem or achieve a goal. In other words, your product helps them get a “job” done. This has been said in lots of different ways.
Clay Christensen of Harvard Business School, has said that “your customers are not buying your product, they are hiring it to get a job done.” Theodore Levitt, also of Harvard, was famous for saying “customer’s don’t want a quarter-inch drill, they want a quarter-inch hole.” Steve Jobs said, that teams should “start with the customer experience and work back toward the technology.” And Thomas Edison said, “Anything that won't sell, I don't want to invent. Its sale is proof of utility, and utility is success.”
These are all the same idea. Your customer has a goal to achieve or a problem to be solved. We now call your customer’s goal/problem a “job-to-be-done” or JTBD. Customers “hire” your product to help them achieve the goal, solve the problem, and get the job done. There are big advantages to defining your market and building your product roadmap using your customers JTBD. First and foremost, your customer’s JTDB doesn’t change over time. Second, you can prioritize where your customer’s struggle the most to ensure you launch features that help them overcome their struggle. And third, your team doesn’t have to use opinions about product ideas in your roadmap. Using your customer's JTBD, you can objectively quantify how each idea helps your customers get the job done.
EXAMPLE
Firing iPods, Hiring Streaming Services
Let’s look at an example. In order to execute the job of “creating a mood with music,” consumers have "hired" a huge range of products: piano rolls, Victrolas, LPs, eight-track tapes, reel-to-reel tapes, cassettes, CDs, MP3 players, and streaming apps. If you define the job with reference to the technologies or products customers have used, you will be trying to hit a moving target. But the job of creating a mood with music has never changed and will never change. This gives you a stable target to hit for your product roadmap.
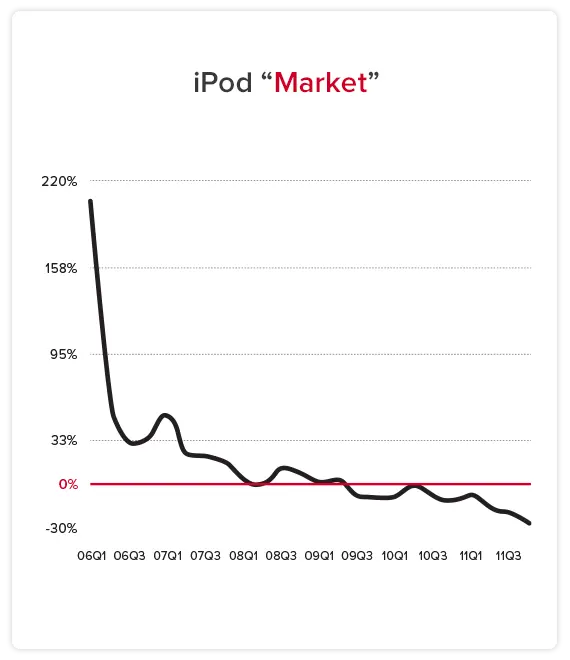
In 2006, Microsoft thought there was a huge opportunity to take share in the “iPod” market. This product-based definition of the “iPod” market led Microsoft to create a product roadmap for the Zune. And it was a total failure. They lost nearly $300 million in one quarter alone. Why did the Zune fail? Because there is no such thing as an “iPod” market. The true market is the customer’s job of “creating a mood with music.”
You can see how Microsoft's fatal mistake was defining (and then sizing) the market based on the traditional market definitions listed here, which all use a product as a critical element. If your TAM or SAM is based on a product, you should redefine them using your customer's JTBD.
We all fired records and hired CDs. Then we fired CDs and hired iPods. Then we fired iPods and hired streaming services. Why? Because the true market is to create a mood with music and each new product got the job done faster and more accurately than the previous. As JTBD shows, the new products were hired because they satisfied unmet customer needs better than the competitive solutions. This is why building a product roadmap using your customers JTBD is so critical. Because it will lead your team to build features that get the job done faster and more accurately than your competitors.
Learn the JTBD Market Definition Technique:
See a Real-World Example:


Market Sizing
Calculating the size of your market accurately is extremely important. Companies that size their market incorrectly risk missing opportunities to accelerate growth and create equity value. History is littered with dead companies that made fatal market sizing mistakes.
TRADITIONAL APPROACH
Product Price Times Number of Buyers
Almost all traditional market sizing equations use the price of your product as a key variable. For example, the Total Addressable Market (“TAM”) is often defined as the number of buyers times the price of a product. Why is this a mistake? Because your customers are not actually “buying” your product, they are “hiring” it to get a job done. As a result, the size of your market opportunity is based on your customer’s willingness to pay to get their job done better, regardless of the price of your product. This is why companies like BlackBerry, Britannica, and Kodak failed when they invested in the wrong product roadmaps. They sized their markets (and thus projected their revenue from their roadmaps) based on the price of their products. How much are you willing to pay for a roll of film or a set of 26 encyclopedias today? Probably $0 because these are both obsolete products.
JOBS-TO-BE-DONE
Your Customer’s Willingness to Pay Is Your Market Size
Remember a critical insight from Jobs Theory: your customers are not buying your product, they are hiring a product to get a job done. Every product in history has been replaced by a new product that got the customer’s job done better. Yours will be too. Defining your market based on your customer's JTBD lowers the risk that your product roadmap fails to generate the revenue growth you need.
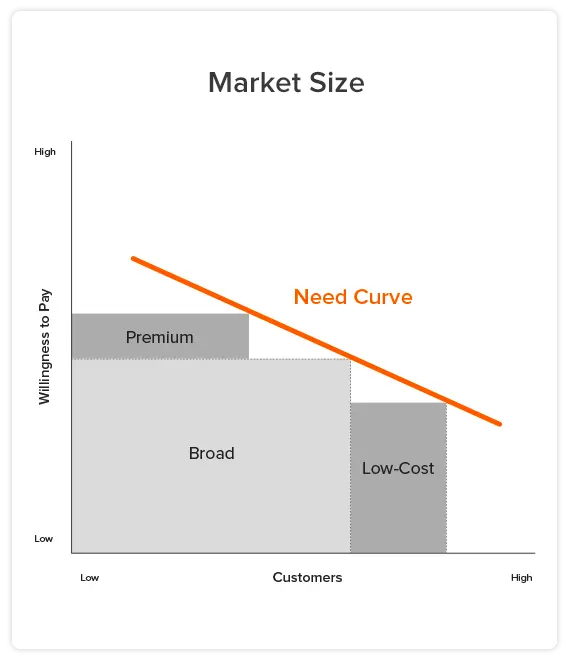
To size a market opportunity, don’t analyze the products currently in the market. Instead, define your market as a goal customers are trying to achieve (a job-to-be-done). You can identify the range of your customers’ willingness to pay to get that job done using a quantitative survey that asks the right market sizing questions. This range of willingness-to-pay can be plotted on a graph from low to high. We call this the Need Curve because it looks like a traditional economics demand curve, but instead of plotting price and quantity of product, it plots the number of customers willing to pay to get their job done. The area under the Need Curve is the size of your market.
If you use the Jobs-to-be-Done framework to size your market, you will be able to justify investments in your product roadmap to ensure that you exceed revenue growth goals. Instead of launching products into markets that are about to disappear, you will be focused on stable markets and where you can win. And you can feel confident that your product roadmap investments will accelerate your company’s growth.
EXAMPLE
From $30 Billion to $0
The market sizing chart shows how the need curve can be used to size your market. It plots different values for customer willingness to pay. The area under the curve is the size of the market. The need curve will be unique in your market, and it will reveal the true size of your market. It determines how much revenue and profit growth you can generate in your market.
Let’s look at an actual example of a fatal market sizing mistake. In 2006, Microsoft thought there was a big opportunity to launch an iPod competitor. They calculated that Apple had sold 200 million iPods at about $150 each. So, using traditional market definitions and market sizing calculations, this was a $30 billion market, which is very large, even for Microsoft. They built a product roadmap of features to compete with the iPod, which even included, ironically, a “podcasting” feature.
The team felt they had a product roadmap that could win because Microsoft had hundreds of millions of existing customers. And their iPod competitor, the Zune, could connect to their Windows operating system, which was by far the dominant operating system in the world. They built out their product roadmap and launched the Zune. It was, of course, a tremendous failure. They lost $300 million in one quarter. And within a few years, Apple’s iPod revenue was effectively $0.
What happened? Did the market go away? Of course not. People are creating a mood with music in larger numbers today than ever before. This is because the JTBD, and thus the true market, is to create a mood with music. In this market, like in all, markets, the leading product, the iPod, became obsolete just like all of the products before it: records, cassettes, and CDs. When a new product emerged (streaming apps) that got the job done faster and more accurately, customers switched to the new product. This happens in every market, including yours. This is why you should use your customers JTBD and their willingness to pay to get the job done as the foundation for your product roadmap. It will ensure that you don’t build the Zune.
Learn the JTBD Market Sizing Technique:
Customer Needs
Satisfying your customer’s needs better than competitors is the key to building your product roadmap. But most companies and product teams don’t agree on what a customer need even is. This is a serious problem that JTBD helps solve.
TRADITIONAL APPROACH
Ask Your Customers What Product They Want
Does everyone on your team agree on how to define a customer need? If you don’t agree, you are not alone. Research has shown that 95% of all companies do not have an agreed-upon definition of a customer need. Without an agreement on customer needs, teams often ask customers about what products they want. This is a mistake. Why? Because your customer’s can’t envision what great product should result from your roadmap. But they can absolutely tell you what problem they need to you to solve, in other words, how they struggle to get their job done.
For example, you could ask 1,000 consumers what products they want and they would likely never come up with the microwave. They don’t have the technical expertise to understand what makes a microwave work. But they can tell you everything about preparing a meal (a JTBD) and how they struggle. This is true in your market too: your customers can explain their struggles, if you know how to frame the conversation.
JOBS-TO-BE-DONE
A Customer Need Is an Action and a Variable in the Job
In Jobs Theory, a customer need is clearly defined, allowing your entire company to communicate in the same way, using the same language when you are building your product roadmap.
A customer JTBD is a goal they need to achieve, independent of any product. For example consumers don’t “want” records, cassettes, or iPods. They want to “create a mood with music.” This is the job-to-be-done. In every JTBD, there are a set of steps that a customer has to take in order to complete that job and achieve the goal. And within each job step, there are actions a customer has to take using variables in the job.
These actions and variables are the customer needs, and like the JTBD they are independent of any solutions. The customer actions in a need are defined by action verbs (e.g. determine, identify, gather, calculate, reduce, ensure, etc.) and the variables are defined by job. For example, in the job of “getting to a destination on time” — the Job To Be Done — the variables include, arrival time, departure time, travel time, the route, alternative routes, traffic, weather, errands, stops along the way (e.g. errands or fuel), etc.
Most JTBDs have 10 to 20 steps and 50 to 100 customer needs. In other words, while your customer’s JTBD is complex, it is knowable. And because the JTBD and the customer needs are independent of any product or service, your customer’s needs are stable over time and will not change. This is the power of JTBD and Jobs Theory: when you are building your product roadmap, your team will have a stable target to hit.
EXAMPLE
How To Identify Customer Needs
Let’s look at an example of how you can identify your customer’s needs. Imagine you are on a product team and you had to beat Apple and Google Maps. The first step is to identify all the needs in the customer’s job of “getting to a destination on time” to make sure your product roadmap is going to result in a product that people want and is better than your competitors -- in this example, Apple and Google Maps.
To identify customer needs, start by identifying the steps in your customer’s JTBD. Job Steps outline what your customer needs to accomplish to achieve the goal (ie. get the job done). And Jobs Steps fall into six categories: understanding steps (i.e. understanding the job or the problem), preparation steps (i.e. preparing to get the job done), execution steps (i.e. taking actions to achieve the goal), assessing steps (i.e. monitoring how well the job is going while executing it), revision steps (i.e. making changes to get the job done better), and conclusion steps (i.e. ending the job successfully).
All jobs follow this job step pattern. For example, getting to a destination on time follows this pattern: An understanding step is to “estimate the departure time.” A preparation step is to “plan the stops.” An execution step is to “travel to the destination.” An assessment step is to “assess if the destination will be reached on time along the route.” A revision step is to “reset the route as needed.” And a conclusion step is to “park the vehicle.” The technique to determine job steps is to ask customers about what process they use to get the job done (i.e. achieve their goal). You can ask them about the steps to understand the goal, plan and prepare to achieve the goal, etc.
Once you have identified all the steps in your customers' Jobs To Be Done, you can identify the customer needs in each step. Ask customers what makes executing each job step difficult, time-consuming or inaccurate. Listen for the variables in the JTBD. For example, when consumers plan stops to get to destinations on time, they have to know variables including the routes to the stops, the optimal sequence of stops, and the open times at the stops. And with each variable, your customer has to take an action. For example, when planning stops a consumer has to determine the optimal sequence of stops.
Since customer needs are metrics, you can survey your customers to identify how much effort it takes them to satisfy their needs. The level of struggle is a Customer Effort Score (CES). If it is too difficult, the effort is high, and the CES is therefor high. You goal is to create customer value by making it easier (faster and more accurately) for your customer to satisfy their needs.
Learn the JTBD Customer Needs Technique:
.webp)

Unmet Needs
Satisfying your customer’s unmet needs with features in your product roadmap is the fastest path to success. The Jobs To Be Done technique emphasizes prioritizing unmet needs in your roadmap to target the most underserved customers.
TRADITIONAL APPROACH
Product Complaints
Companies often do market research to figure out what customers want. These methods include NPS (net promoter scores), customer opinions about product features, or trends like emerging technologies (e.g blockchain). But there are critical flaws in these methods: they don’t focus on your customer’s struggle to get their job done independent of any product, service, or technology. The iPod had very high NPS scores, but this didn’t help Microsoft launch a successful competitor because it didn’t show them where customers were struggling to “create a mood with music” (the JTBD).
If you ask customers about products, they will give you answers about products. This is what Henry Ford meant when he famously said “If I asked customers what [product] they wanted, they would have said a faster horse.” Instead of asking customers about your product (or your competitor’s) ask them about their struggle to get their job done. This is how you can identify unmet customer needs, and segment customers based on their unmet needs. This is the key to your product roadmap’s success.
JOBS-TO-BE-DONE
Quantify Your Customer’s Unmet Needs with a Survey
Customer needs are powerful because they are quantifiable. Every customer need in your customer’s JTBD has an action and a variable that are independent of any product. For example, no one needs the “Add a stop” feature in Google Maps. What they need is to “determine the optimal sequence of stops.” In this example, “determine” is the action and “optimal sequence” is the variable. And in every JTBD, your customers want to get their job done as fast and as accurately as possible. As a result, you can measure the speed of your customer’s action and the accuracy of the variable in every need.
In order to determine which customer needs are unmet, you should conduct a customer survey and ask customers if it is difficult for them to satisfy the need today. For example, how difficult is it for consumers to determine the optimal sequence of stops in their day? If it is difficult, consumers will tell you in the survey. And if a high enough percentage of customers say the need is difficult to satisfy, then the need is an unmet customer need. This makes sense because customers who struggle (i.e. who say it is difficult to satisfy the need) are the ones most likely to buy the features you build in your product roadmap that satisfy the need faster and more accurately (i.e. with less customer difficulty). You can think of your survey results (i.e. the percentage of customers who struggle) as the probability that customers buy what you are building in your product roadmap.
EXAMPLE
Using Unmet Needs to Beat Apple and Google Maps
If you were building a product to beat Apple and Google Maps, you would want to know where customers struggle the most. In a survey, 86% of consumers said that determining the optimal sequence of planned stops in a busy day was difficult with Apple and Google Maps. It is not hard to see what this is true.
For a busy person with multiple meetings, appointments, and errands throughout a day, determining the optimal sequence using Apple Maps or Google Maps would require entering destination A, calculating the time and the route to destination B. Then entering destination A, calculating the time and the route to destination C, comparing the two A to B and A to C routes, determining which was quicker and repeating the process for every possible combination of destinations.
With Apple Maps and Google Maps satisfying the need to determine the optimal sequence of planned stops is manual, time-consuming and likely highly inaccurate. It is not surprising that 86% of consumers said it was difficult. This is the power fo JTBD: you now have a quantifiable unmet customer need you can use in your product roadmap. The probability that consumers adopt your new solution to satisfy this need is high if you help them overcome their struggle.
You can do this analysis for every need in your customer's JTBD to ensure that your product roadmap is focused on satisfying unmet needs better than your competitors.
Learn the JTBD Unmet Needs Technique:


Product Strategy

Every product roadmap is the result of a product strategy. Choosing the wrong product strategy can be fatal. Just ask all the failed companies throughout history.
TRADITIONAL APPROACH
Performing Activities Differently from Competitors
A product strategy is a plan to beat your competitors. How do you create a strategy? In 1996, Harvard Business School Professor Michael Porter wrote a famous paper called “What is Strategy?” Companies often use Michael Porter's definition of strategy, since he was a pioneering academic in the field, famous for analyzing industries to determine competitive strategy. In Porter's view, “The essence of strategy is choosing to perform activities differently than rivals do.” Activities can include manufacturing, engineering, distribution, marketing, and selling.
What is missing from these “activities” is your customer. This is why Porter’s definition is outdated: he didn’t include your customer’s job-to-be-done in his definition of strategy. Your customer’s needs, not your activities, should be the focus of your product strategy. Your customer does not care about your activities. They care about getting their job done.
JOBS-TO-BE-DONE
A Product Strategy Is Your Choice of a Target Customer, JTBD, Segment, and Unmet Needs.
Creating a successful product strategy includes making four choices.
First, which customer are you going to target? As we said above, markets evolve to remove Job Executors as Job Beneficiaries can get more of the job done without their help. Targeting the Job Beneficiary with your product strategy is a stable, long-term choice. In some markets, Job Executors are still critical to getting the job done because the technology cannot yet get the job done without them. In this case, you might choose to target the Job Executor to create short-term growth. The key is to understand the risks of your customer target decision and align your team with a clear target customer to create focus.
Second, which job-to-be-done are you going to target? Your customer’s job is your market. Choosing an underserved job that customers are willing to pay to get done better is the foundation of your success.
Third, which customer segment will your focus on? You want to focus on a group of people who struggle significantly with the job, have unmet needs you can satisfy, and are willing to pay enough to overcome them that you can achieve your growth goals by only focusing on this segment.
Fourth, which unmet needs will your product, marketing and sales teams focus on? Prioritizing the unmet needs in your target customer segment is the key to accelerated growth and faster equity value creation. This last point is the most important. You will be surprised by how much your teams can achieve when they are tightly focused on an underserved customer segment with unmet needs.
EXAMPLE
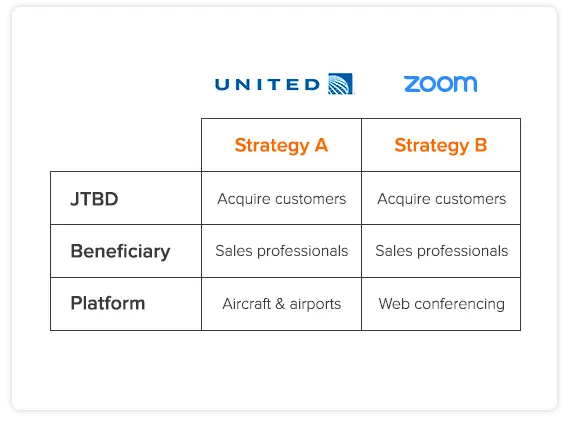
Airlines vs. Video Conferencing, Zune vs. Pandora
JTBD product strategy is very powerful because it can reveal unseen competitive threats. For example, United Airlines likely doesn’t think that video conferencing is a strategic threat. But if you analyze one of the airline's most important customers --salespeople, and their job-to-be-done -- you can see the threat. Salespeople are hiring airlines to acquire customers. They can also hire video conferencing to get the same job done. The unmet needs each company chooses to target in this job will drive the designs of their solutions and which salespeople choose which solution. If video conferencing satisfies all of the needs better, it will take this profitable customer segment away from airlines.
Which one will win? The coronavirus pandemic and lock down just accelerated what was already happening. Web conferencing is getting better (and will continue to get better) at helping salespeople acquire customers without the need to get on a plane. These customers are very valuable to airlines, so web conferencing is a serious competitive threat to airlines.
You can also see why JTBD product strategy is effective when analyzing products that changed over time. Microsoft and Pandora had the same product strategies, targeting the same customer (consumers) and the same JTBD (create a mood with music). But, Microsoft chose the same solution platform as the iPod (a hard drive device), while Pandora chose a different platform (streaming to apps). The product roadmap for Microsoft’s Zune resulted in a $300 million loss in one quarter alone, while Pandora’s product roadmap helped them grow to 90,000 new users per day. In this example, a streaming platform clearly satisfied the unmet needs in the job faster and more accurately. If Microsoft had a clear JTBD strategy in focus instead of trying to take share of a product-defined market (MP3 players), it may have recognized that the Zune would not satisfy needs in the job any better than the iPod and streaming would satisfy needs much better. This is the key to JTBD strategy: putting your team's focus on customers' unmet needs in the job helps them make solution choices that leapfrog competitors.
Learn the JTBD Customer Technique:

Competitors

To beat your competition, identify where they get your customer’s job done slowly and inaccurately. Using JTBD, you can beat even the biggest competitors in the world.
TRADITIONAL APPROACH
Feature-to-Feature Comparisons
In traditional competitive analysis, product teams often compare their own product's features to a competitor's features. If Product A has all of the features of Product B plus a few more, then Product A has the advantage. More features equals more competitive advantage.
Focusing on feature-to-feature comparison is the wrong way to think about competitive differentiation. Why? Because your customers don’t want more features, they want your product to help them get their job done faster and more accurately. Microsoft’s Zune had more features than Apple’s iPod, yet it failed to take any meaningful share of the market because it didn’t get the job done faster or more accurately. Streaming services (like Pandora and Spotify) actually had fewer features, but they got the job of “creating a mood with music” done much faster. Pandora only had one end-user feature: click play to listen to music for the mood. Pandora’s algorithms did the rest.
If you've ever been on a team that is playing feature catch-up, you know it's like bailing water out of a leaky boat: every time you release a feature and think your work is done, your competition releases something new, racing ahead of you yet again. You will always be a step behind.
JOBS-TO-BE-DONE
Identify Your Competitors' Weakness Using Unmet Needs
Your customers are analyzing your competitors every day. When they struggle to get their job done, they’ll look for new competitive solutions to get their job done faster and more accurately. In Jobs Theory, a competitor is any solution that helps get a job step done. This approach can help you identify your real competitors in each job step, as opposed to relying on industry-based competitors.
Competitive weakness is satisfying a need slowly or inaccurately. Since needs are structured with an action and a variable, you can measure the speed of the action and the accuracy of the variable when customers use your competitor’s solution. You can use the JTBD analysis to analyze not only your competition, but also your existing product in order to identify where it needs to be improved. As a result, you can add those improvements to your roadmap before a competitor attacks your product and takes your market share by getting the customer's job done faster and more accurately.
EXAMPLE
Planning Stops With Apple and Google Maps
Imagine you were trying to build a product to beat Apple and Google Maps. How would you analyze these products to figure out what features you should put in your roadmap?
People hire maps applications to “get to destinations on time.” One of the job steps is to plan the stops. And if you have a busy day with multiple stops, you need to determine the optimal sequence of stops to make sure you stay on time with your meetings, appointments and errands.
“Determine the optimal sequence of stops” is a customer need in this job-to-be-done. It has an action (determine) and a variable (the optimal sequence). To analyze Apple and Google maps, you assess the speed and accuracy of determining the optimal sequence using those products.
If a user were to try to determine the optimal sequence of stops using Apple or Google Maps, it would take multiple steps. For example, a user would enter destination A, enter destination B, calculate the route and time, repeat for destination A to C, re-plan if going from A to C first was faster and less variable, and repeat this process for all possible combinations of stops. This manual process is very slow and the accuracy is low if the user could even successfully determine the optimal sequence at all.
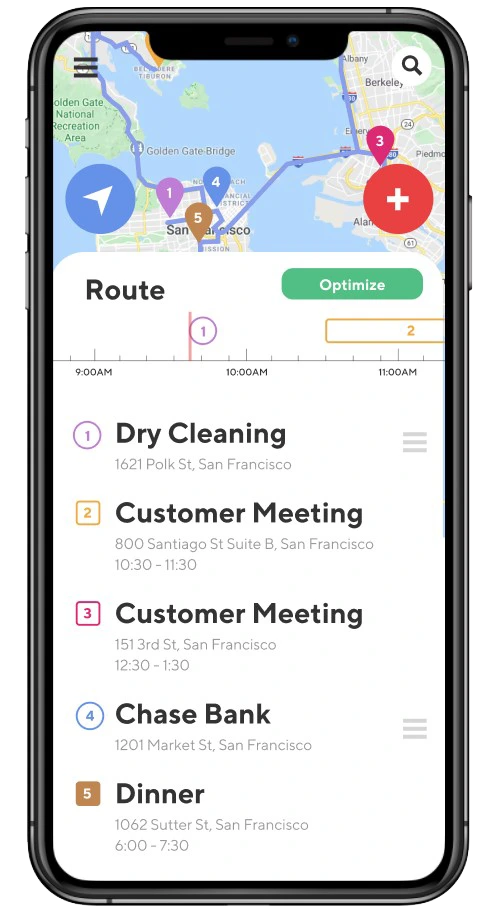
This is a weakness in Apple and Google Maps. You can do this analysis with your competitors (and your product) to identify where your customer struggles to get their job done with the competitive solutions in the market. Remember, a competitive solution is anything that helps a customer get a job step done and satisfy customer needs in the job. In the image on the left, you can see all the steps in the job of getting to a destination of time, each with a competitor overlaid on the job step. This helps you visualize your competition, and it reveals which job steps have fewer competitors.
Learn the JTBD Customer Technique:


Segmentation

To accelerate your growth and win in your market, you should identify the most underserved segment of customers. But how you define this segment will determine your ultimate success or failure.
TRADITIONAL APPROACH
Demographic characteristics
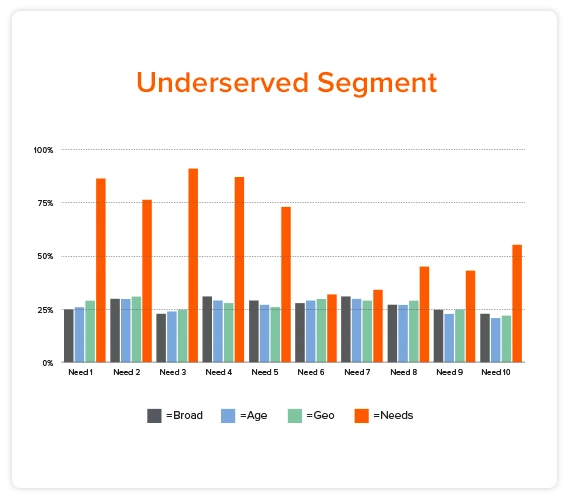
You have probably used traditional segmentation characteristics like demographics (age, zip code, gender, etc.), psychographics, purchase patterns, or industry verticals (in B2B markets). But this almost never works because characteristics like age and zip code do not determine if your customers struggle to get a job done. In JTBD segmentation, you use your customer’s unmet needs to identify the most valuable segment, regardless of their characteristics.
For example, “getting to a destination on time” is a JTBD (it is a goal consumers need to achieve independent of any products). Could an urban woman with a Ph.D. struggle to get to a destination on time the same way a younger, rural man with a high school education? Yes, of course. And the reason they both struggle is not because of their demographics or characteristics, it is because they both struggle with something specific, like making frequent and unfamiliar stops.
JOBS-TO-BE-DONE
Segment your customers using needs in their job
The core idea in Jobs-to-be-Done (JTBD) is that your customer’s struggle to get their job done is what causes them to make a purchase. The most valuable customer segment is the group of customers who struggle the most and are willing to pay the most to get their job done better.
Customers buy new products because they struggle to get a job done at a price they are willing to pay, regardless of their characteristics like demographics, geography or psychographics. JTBD segmentation identifies the group of customers in your market who struggle the most and who are willing to pay the most to get the job done better. This ensures that your product will be a success because you will be targeting the customers who need it the most.
Most importantly, with JTBD you can collect data to guide your segmentation. In a Jobs-to-be-Done survey, you can get quantitative insights into which customer segments struggle the most, how many customers are in the segment, and how much they are willing to pay to get the job done. Using profiling questions, you can segment customers by profiling characteristics and find out for yourself if Jobs Theory holds up. Or perhaps you’ll get lucky and find a profile-based segment that struggles more than others and represents a big enough market size. Most often though, you’ll find that the struggle is not different across profile-based segments. The good news is that because of the survey, you have data to prove this to your team and to help you find a struggling segment, independent of profiling characteristics.
EXAMPLE
Who struggles the most to get their job done?
Let’s look at an example. Imagine your product team is trying to beat Apple and Google Maps. Which users of Apple and Google Maps would most likely switch to a new product? Using traditional segmentation characteristics doesn’t tell you who these customers are. But when you survey people who need to get to destinations on time using customer effort scores you can quantify which customers struggle the most. The underserved segment is the group of customers with the highest customer effort scores (i.e. the most unmet needs in the market). You can then create personas of these underserved customers using their unmet needs. For example, the customers who would most likely switch to a new product from Apple and Google Maps are customers who make frequent and unfamiliar stops. They struggle to plan their stops (a job step) and they struggle to determine the optimal sequence of stops (a customer need). And they are willing to pay for a new solution that satisfies their unmet needs. You now have identified a valuable customer segment, and if you build a product to satisfy their unmet needs faster and more accurately than Apple and Google Maps, there is a high probability that they will buy and use your new product.
So who are the customers to target in this market? Who struggles to get to a destination on time? This example shows why creating customer personas to define your customers can be flawed. Could two different customers with very different personas and characteristics, both struggle to get to a destination on time. The answer, of course is yes. And the reason they each struggle has nothing to do with their persona characteristics. It has to do with the nature of the how they execute the job. In this case, they both struggle to get to destinations on time because they both make frequent and unfamiliar stops. In other words, these two very different customer personas actually have the same unmet customer needs in this market.
Learn the JTBD Customer Technique:

Idea Generation

Your team’s product ideas for your roadmap are critical to your success. How do you generate and analyze the best ideas for your roadmap before your team invests in product development?
TRADITIONAL APPROACH
Brainstorming
To facilitate the generation of new ideas, product teams often rely on brainstorming. And in those brainstorming sessions, there is often only one rule - there are no bad ideas. In other words, your team is not supposed to use any criteria to judge new ideas on the assumption that this will enhance creativity.
Often these ideas can come from customer requests, sales team requests, stakeholders, or new technologies. The possibilities are endless, which is the problem. The reason brainstorming is inefficient is because there are no objective criteria to quickly and efficiently judge new product ideas. And those criteria are the unmet customer needs in the job.
JOBS-TO-BE-DONE
Direct your ideation process with customer needs
When generating ideas, you can use your customer's unmet needs to quickly evaluate competing ideas using speed and accuracy. If you have aligned with your team on a high-growth product strategy, then you have a key customer, target segment, and unmet needs in the job in focus. Your goal with new ideas is to satisfy the target unmet needs faster and more accurately than competitors in the market.
Once you have a need in focus, you can assess the speed and accuracy of competitor solutions to set the benchmark your new idea should beat to get customers to switch from their current solution to yours.
You can then assess the speed and accuracy with which your new ideas will help customers satisfy the target needs. If a new idea is faster and more accurate in concept, you know it’s worth further examination: assessing the cost and risk, testing prototypes with customers to confirm they perceive the value, etc.
EXAMPLE
Which idea will beat Apple and Google Maps
To continue with our Apple and Google Maps example, if you are going to generate and evaluate product ideas to beat competitors, you should start with your customers' unmet needs. The unmet needs are the criteria to judge any idea your team may have. Before generating or evaluating product ideas, you should have a detailed description of the customer you are targeting (in this example, drivers), the job they are trying to get done (e.g. get to destinations on time), the undeserved job step in the segment (e.g. plan the stops) and the unmet need (e.g. determine the optimal sequence of stops).
With the job step and the unmet need in focus, your team can generate and analyze ideas. For example, let’s say your team had two competing product ideas to satisfy the need to “determine the optimal sequence of stops.” The first idea is an Assistant Service where a user calls a virtual assistant and gives them access to their calendar. The assistant would look up the relevant traffic information, construction information, event information, weather, etc. around the destinations for the date and time of the meetings. The assistant would then make changes to the calendar. The second idea is Sync and Optimize, where the user syncs their calendar to an app that uses relevant information inputs and optimization algorithms (e.g. “traveling salesman” algorithms) to determine the optimal sequence of stops to keep users on time for their meetings. This is the process to generate and analyze product ideas in order to determine which ones will create the most customer value before investing in new product development. Now that your team has multiple product ideas that target unmet customer needs, you can use speed and accuracy to determine which one will create the most customer value.
Learn More About JTBD Idea Generation:
Customer Value

Creating customer value is the key to your team's success. Products that create more customer value take share from competitors and win in markets. But what is customer value, and how is your team measuring it? How should you use customer value to prioritize your roadmap?
TRADITIONAL APPROACH
Using NPS and satisfaction scores as a proxy for customer value
In traditional methods, companies use Net Promoter Scores (NPS), satisfaction, and other metrics to help determine the customer value of the product. While NPS and satisfaction may give your team data about your customers’ view of your product, they don’t identify where your customer is currently struggling. In other words, because NPS are focused on your product, they don’t identify your customer’s unmet needs. The iPod, for example, had extremely high NPS and satisfaction scores, but that did not help identify the opportunity for streaming services, which now dominate the industry and ultimately killed the iPod as a platform for creating a mood with music (the job-to-be-done).
Traditional methods don’t give your team insight into why customers are dissatisfied or how you can add more value. In addition, if you’re launching a new product that hasn’t been used by customers, how can you determine if it will provide value to customers?
JOBS-TO-BE-DONE-THEORY
Calculate your feature’s speed and accuracy
Your ultimate goal as a company is to satisfy your customer’s needs better than competitors in your market. Your customer’s struggle to get their job done (i.e. their struggle to achieve their goal independent of your product) is what causes them to purchase a new solution. So customer value is providing your customers with a solution to overcome their struggle faster and more accurately than your competitors.
The ultimate customer value is provided when you help your customers get their job done with less effort. To mitigate the risk of product failure, you can measure customer effort and customer value before investing in product development. Your product will create customer value if it gets the job done faster and more accurately. And speed and accuracy are metrics you can measure even before you invest in product development. If your new product idea is not significantly faster and more accurate, your team should keep iterating the idea. You want to help your customers get the jobs done in their life easier. Life is hard enough already. Make life easier for your customers. This is your goal. Once you have created product ideas with significant customer value, you should prioritize these in your roadmap.
EXAMPLE
iPod vs. Zune vs. Streaming
Let’s look at the iPod example again. In 2006, the iPod dominated the world of MP3 players. iPods came to dominate because they helped consumers create a mood with music faster and more accurately than the CDs which they replaced. For consumers to create a mood with music (the JTBD) with CDs, they had to travel to a music store like Tower Records, browse CDs, purchase a CD, play a song on the CD, switch to another CD to play a similar song from a different artist for the mood. They could record the songs from CDs to cassettes, which had a limited amount of time, about 90 to 120 minutes of music. When CDs dominate the world of music, you could measure the speed and accuracy of getting the job done. The whole process could take hours, even days, and because consumers had to buy whole CDs to get just one song they liked, it was not very accurate when creating a mood with music.
Apple’s marketing message for the iPod was “1,000 songs in your pocket.” And like all innovation that succeeds, the iPod got the job done faster and more accurately. With the iTunes Store, consumers could browse and preview songs for the mood they were creating. This made getting the job done more accurate and lower cost because they didn’t not have to buy whole albums when they only wanted one or two songs by the artist. And it was much faster because they could buy songs from the iTune stores without any travel to a traditional “brick and mortar” retail location.
In 2006, Microsoft launched the Zune, and iPod competitors. The Zune is an excellent example of a product that did not create any customer value. In other words, it worked almost exactly like an iPod. A user visited an online store, purchased and downloaded songs, and synced those songs to their Zune. If Microsoft had analyzed the customer value of the Zune using speed and accuracy, it would have been obvious that they should not invest in its product development because it was not faster or more accurate than its competition.
But streaming services, starting with Pandora and eventually Spotify. Took a different approach. A consumer didn’t need a dedicated device to create a mood with music, and they didn’t even have to purchase and download songs. Pandora enabled a user to select an artist or song for the mood, click play and listen to an almost limitless number of songs for the mood. Their algorithms were very good at identifying the mood and a user could refine the algorithm by simply clicking thumbs up or down for each song. Clearly streaming services were faster and more accurate than the iPod and the Zune. When the Zune launched, Pandora was signing up 90,000 users per day, and streaming services now dominate the music industry.
Learn the JTBD Customer Technique:

Product Roadmapping

Prioritizing features on your roadmap is the key to beating your competition, accelerating your revenue growth, and creating equity value for your company. The Blackberry and the iPhone both had product roadmaps. One led to the destruction of $50 billion, the other led to the most successful product and company in the history of business.
TRADITIONAL APPROACH
Gather requirements from stakeholders
Traditionally when product teams “own the roadmap,” they aggregate feature ideas from your company’s stakeholders. Prioritization of features can become a political battle between personalities on your team because there are no objective customer criteria to serve as the basis for your team’s decisions. In short, your team should not prioritize your roadmap, your customers should. Blackberry failed because they did not understand the unmet customer needs in their market, and as a result, they prioritized their product ideas (about improving a keyboard-based device), rather than prioritizing feature ideas that would satisfy unmet needs faster and more accurately.
JOBS-TO-BE-DONE-THEORY
Prioritize your roadmap with your customer’s unmet needs
To prioritize your roadmap, your team first needs to agree on your product strategy, making clear choices about:
- Your target customer
- The job-to-be-done you help the customer get done
- An attractive target customer segment
- The size of the customer segment
- The probability of generating the revenue growth you need
- The unmet needs you satisfy to get the job done better than competitors
Having the strategy in focus gives your team objective criteria to judge the ideas on the roadmap.
Next, you need to assess everything on your roadmap in light of your product strategy.
Categorize backlog items as follows:
- Tech Debt
- Customer Commits
- Maintenance/Bug Fixes
- On Strategy Product Ideas
- Off Strategy Product Ideas
Different teams have different names for each of these categories but every roadmap has some version of them. The goal in this assessment is to determine what percentage of your resources are allocated to each category and if that allocation will achieve your growth goals.
The more aggressive your growth goals, the larger percentage of your resources should be allocated to On Strategy Product Ideas. To determine if an idea is on strategy, you need to answer the following questions related to your strategy:
- Does the idea help our target customer segment get the job done?
- Does the idea satisfy a need for a high priority job step in your strategy?
Customer Commits and On Strategy Product Ideas are not mutually exclusive. You could have a customer request a feature that fits well with your strategy.
But, you need to be aware of those customer feature requests that are off strategy. They can help you get short-term revenue, but they can throw you far from your strategy and cause you to miss the biggest opportunities in your market.
EXAMPLE
Blackberry over-allocated resources to customer commits
Blackberry is an example of a company that likely allocated a tremendous percentage of their resources to customer feature requests, but they missed the unmet customer needs that could be satisfied without a keyboard, faster and more accurately with a touch interface. Because they were focused on their product (a keyboard device) and customer requests about improving that device, they missed the opportunity to prioritize their roadmap based on the unmet needs in their customers’ jobs-to-be-done. As a result, Blackberry failed to capitalize on the biggest market opportunity in the history of business.
Learn the JTBD Customer Technique:

Positioning

Creating a unique and clear position in the market for your product is extremely important. It helps you differentiate from your competitors and conveys a unique value proposition to your customers. Good positioning makes it easier for your customer to make the decision to buy your product.
TRADITIONAL APPROACH
Position your product by its features
When companies come up with a positioning strategy, traditional methods (for example as explained by Harvard’s Michael Porter) are often driven by cost or feature differentiation and broad or narrow customer focus. Accordingly, you can choose to be the low cost solution or a feature differentiated solution. If you are focused on being the low cost solution, competitors can copy your operational effectiveness as best practices disseminate in your industry. If you position your product based on the feature differentiation, it will supposedly help differentiate your product enough so that customers are more likely to buy it. However, what happens when a competitor comes along and highlights the same set of features and benefits? You’ll constantly be playing catch up, trying to compete with similar products.
JOBS-TO-BE-DONE-THEORY
Position to the job steps and unmet customer needs
It can be a struggle to come up with a unique position in a crowded market. However, Jobs-to-be-Done can help you create a positioning plan that connects with customers quickly. The key difference in JTBD positioning is that you don't use the product features to position the brand or product. Instead, you look at the steps a customer takes to get a job done and you focus on those steps that are the biggest struggle for customers. In other words, those steps that have unmet customer needs.
EXAMPLE
Positioning against Apple and Google Maps
As an example, if you were competing with Apple and Google Maps, you face competitors with almost 100% market share, almost limitless resources, and built in competitive advantages (because their maps applications are included for free with their platforms). It would be very hard to position and compete on cost when the competitors are free. How would you position against them in order to differentiate? The customer's JTBD in this market is to “get to destinations on time.” This JTBD has 16 different steps, including “planning the stops.” JTBD analysis shows that there is a large segment of underserved customers who struggle to plan their stops because they make frequent and unfamiliar stops. Positioning to this job step is an effective way to target these underserved customers and differentiate from Apple and Google Maps because their solutions do not quickly and accurately help customers plan their stops in a busy day with unfamiliar destinations.
Learn the JTBD Customer Technique:

Messaging

The best product in the world won’t generate growth if no one knows about it. Craft messaging that resonates with unmet customer needs in the job-to-be-done to convert leads to customers.
TRADITIONAL APPROACH
More features and technology is better
Comparing features and specs across competitors is everywhere. We’ve all seen the table that shows a bunch of features down the left and then checkmarks for each competitor who has each feature. More features=better, right? The problem is customers don’t know what features they want, they know what problems they want to solve. As Henry Ford put it, “If I asked customers what they wanted, they would have said a faster horse.” The horse riders know they want to get to their destination faster but they don’t know what features and technologies will make it happen. This is also true today. Telling your customers that your product has AI does not help them understand why that’s valuable.
JTBD THEORY
Message to the emotions of getting the job done better
Empathizing with your customers means recognizing that your customers don't want to use your product features, they want to get the job done so they can get back to their lives.
The trick is to include 3 elements:
- The job you help customers get done
- The functional and emotional struggle with getting the job done that you will help them overcome
- Demonstrate how your solution helps them overcome the struggle quickly and accurately
In other words, let your customers know that you understand their problem and show how your product helps them solve it.
We have seen this messaging technique improve marketing effectiveness 10x over product and feature-based messaging.
EXAMPLE
Kodak Brownie
At the end of the 19th century, photography was extremely onerous. Not only did you have to take the picture, you had to develop it using a wet plate collodion process, which was as hard to do as it was to say. It was a time-consuming and sensitive process involving large equipment and mixing chemicals, largely left to experts. In 1900, Kodak launched the Brownie with the slogan “You press the button, we do the rest.” Not only was the product a major innovation in terms of improving the speed and accuracy of preserving a memory, but the message was a classic example of telling the customer you will get the job done for them.
Learn the JTBD Technique: